It is difficult to generalise about implementation of responsible investment in private debt as the latter comprises so many different investment strategies.
Instead, we have identified the main characteristics of various private debt strategies. In the section A framework for responsible investment in private debt we explain how these characteristics relate to different responsible investment approaches.
Figure 9: key characteristics of various private debt strategies
| Private debt strategy/type | Description | Typical credit rating | Flexibility of terms | Stakeholders(excluding borrower) | Availability of public ESG data and related ESG research | Extent of lender influence | Level of liquidity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Leveraged loans |
Loans made to companies typically to finance acquisitions, mergers and leveraged buy-outs by private equity sponsors and other leveraged owners. |
High yield |
Fixed |
Multiple investors |
Good for public companies |
Medium |
Average |
|
Private placement |
Unlisted debt securities typically issued by investment-grade (and occasionally sub-investment grade) companies to a select group of investors. Structured as bonds, notes or loans. |
Investment grade/high yield |
Fixed |
Multiple investors Deal arranger |
Poor for private companies |
Low |
Illiquid |
|
Syndicated loan |
Loans arranged by banks or other entities on behalf of a single borrower, offered to a group of lenders (a syndicate). |
High yield |
Fixed |
Multiple investors Deal arranger |
Poor for private companies |
Low |
Illiquid |
|
Unitranche |
A hybrid loan structure that combines senior debt and subordinated debt risk into one single senior loan with a blended interest rate, without the use of intermediaries such as banks. |
High yield |
Flexible |
Single or small number of investors |
Poor for private companies |
Medium |
Highly illiquid |
|
Distressed debt |
Investments in debt of entities in financial distress with the expectation of participation in the upside of the entity recovering. |
High yield |
Flexible |
Single or small number of investors |
Poor for private companies |
Medium |
Illiquid |
|
Public debt/Bonds |
Debt instruments which are tradeable on an exchange. Issuers include government-related entities, banks, corporates and special purpose vehicles (SPVs) created to finance projects or asset pools. |
Investment grade/high yield |
Fixed |
Multiple investors |
Good for public companies |
Low |
Liquid |
|
Corporate direct lending |
Loans to conservatively managed mid-sized companies made on a bilateral basis without the use of intermediaries such as banks. Every deal has a unique negotiated structure. |
Investment grade/high yield |
Flexible |
Single or small number of investors |
Poor for private companies |
Medium/low |
Illiquid |
|
Mezzanine debt |
A hybrid of debt and equity financing that is comprised of subordinated to senior debt. |
High yield |
Fixed |
Single or small number of investors |
Poor for private companies |
Medium |
Highly illiquid |
|
Infrastructure debt |
Typically long-term project-type debt investments used to finance development, upgrades or ongoing maintenance of infrastructure assets. |
Investment grade |
Fixed |
Multiple investors |
Poor for SPVs |
Medium |
Liquid |
|
Real estate debt |
Typically long-term project-type debt investments used to finance development, upgrades or ongoing maintenance of property assets. |
Investment grade |
Fixed |
Multiple investors |
Poor for SPVs |
Medium |
Liquid |
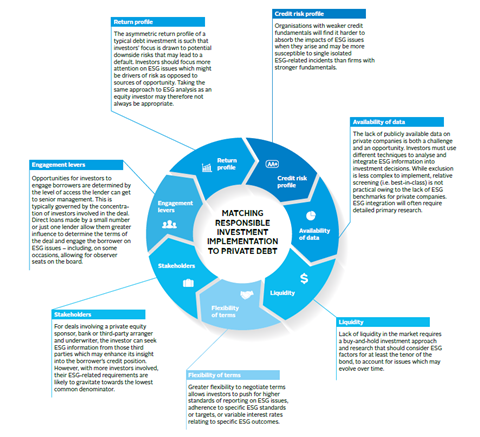
Spotlight on responsible investment in private debt
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
 Currently reading
Currently readingResponsible investment and private debt
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10